Smartphones have become a necessity for us in the new era. We’re used to convenience and on-demand resources. We’re entering a period in which “anything is possible.” The advancement of mobility gives smartphones great capabilities and procreant ground for various mobile apps. We are seeing significant expansion, with new inventions surfacing on a daily basis.
According to a research report, mobile apps have continuous growth and popularity accelerated during the time of global pandemic and shifting demands over how and when users interact over mobile. Thus, according to the “Mobile App Development Trends in 2023” report shows that app installs were 31% year-over-year and 4.5% was counted as user engagement. In total there are over 2.22 million apps on the Apple App Store and over 3.48 million applications on Google Play Store.”
Today, due to the introduction of 5G devices, there is driving demand for new applications with post-pandemic device behavior sticking around, including the driver for shopping convenience and delivery services as well as free time fillers. Whether it’s about gaming apps or home fitness applications.
Detailed Architecture of Mobile App Development:
Mobile App Development Architecture is a set of techniques and patterns required for building a fully structured mobile app. Such patterns are formulated by keeping the client’s requirements and by keeping the industry standards in mind. Thus, in simple words the app development architecture embraces a set of patterns which can build a fully structured mobile app.
App’s architecture refers to a framework in which an app is well structured and organized. The architecture basically includes the app’s overall design, the way its code is organized and the specific technologies and frameworks that are used. It is a collection of models and technologies, to create fully structured mobile applications that finally adhere to the vendor and industry-specific standards.
It is always said to have a well-designed mobile app architecture which improves the app’s performance, stability and also scalability. There are a few principles that should be followed to create compelling architecture. One of the most crucial factors to consider is keeping the codebase modular. This means dividing the code into distinct parts that can be easily maintained and updated independently of each other. Another fundamental principle is to use standardization wherever possible. This helps to ensure that the different parts of the codebase are compatible with each other and that new updates can be easily integrated.
Mobile App Architecture Layers:
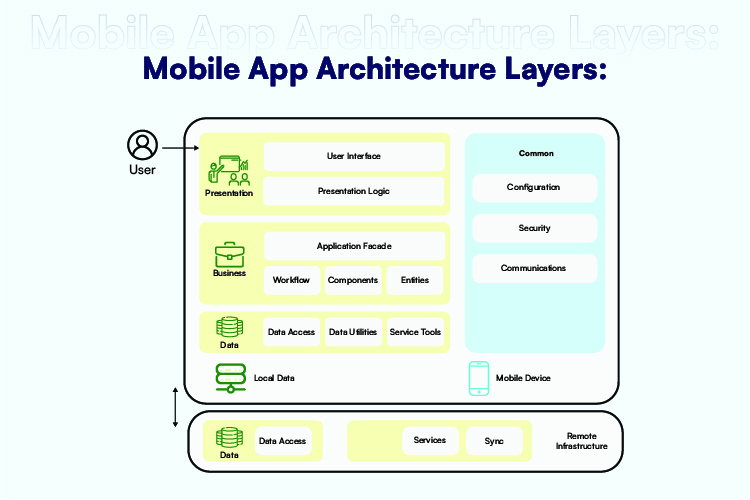
The architecture is divided into three layers: the presentation layer, the business layer, and the data layer.
Let’s take a closer look at these layers.
1. Presentation Layer:
This layer is the face of the mobile application and comprises of UI/UX design. The user sees and interacts with this layer; it is also critical to ensure that the presentation layer is precisely designed and user-friendly. Developers, on the other hand, are concerned with what the user sees and feels while using the application. As previously said, the layer is comprised of UI and UX, with UI being concerned with design, colours, fronts, and the general look of the program. UX manages how users engage with the app by developing a thorough grasp of what the user wants and feels.
2. Business Layer:
The logic and rules responsible for data interchange, operations, and workflow regulations are dealt with in this layer. This layer is mostly in charge of:
- Protection
- Caching of data
- Recording
- Data verification
- Management of exceptional cases
The business layer is separated into multiple sublayers, each of which is responsible for a certain task. Sublayers are also in charge of responding to network requests, managing local data, and processing user input. The layer is known as the mobile app’s heart, where all vital data and logic is housed. However, in any mobile app architecture, the business layer oversees and manages data flow between the user interface and the data access layer. As a result, the layer comprises the app’s functionality and is thus the most sophisticated portion of the program.
3. Layer of Data:
This oversees storing and retrieving data as well as managing data-related operations such as synchronization and caching. All data utilities, service agents, and data access components that facilitate data transactions are included in the data layer.
This layer is divided into two parts namely, Persistence and Network. Persistence where data is accessed via API to data sources and in Network is meant for communication, routing and error reporting. Thus, the architecture of data layer must include considerations for data validation and maintenance.
It is critical to consider the needs of an app and its users while creating a data layer. For instance, if an app demands real-time data updates, it should be structured to do so. Alternatively, if an app simply needs data that is updated on a regular basis, a simpler architecture may suffice. The goal is to construct an efficient and dependable data layer.
IOS & Android Development Architectures:
Two major types of mobile app development architectures, which are the most popular for ages.
Architecture of iOS Mobile Apps:
To construct native iOS apps, Objective-C and Swift are needed, and Apple clearly explains recommended procedures for app development using the Model-View-Controller paradigm (MVC). This pattern decouples data presentation from the business logic that drives an app. The data layer is represented by the Model. The View layer is in charge of displaying data to the user, whereas the Model layer houses the data as well as the business logic. The Controller is a mediator level that communicates with an abstraction via a protocol.
This model makes the codebase easier to understand and maintain. It also allows developers to reuse components across different app parts.
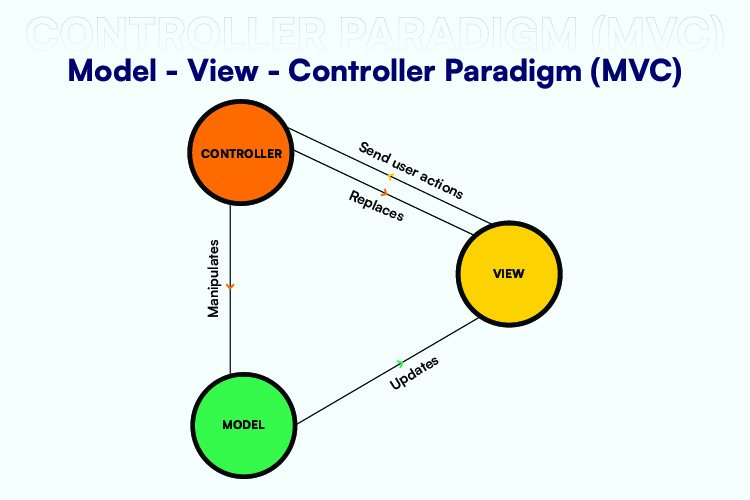
Model-View-View-Model (MVVM) is another common architectural style. This design is like MVC, however there are a few important distinctions. First, the View layer is not in charge of handling user input; instead, this is assigned to the View-Model layer. Second, the View-Model offers bindable properties that the View layer can use to update itself automatically as data changes. This model leads to a codebase that is more testable and maintainable. Finally, it simplifies the creation of reactive user interfaces.
Architecture of Android Mobile Apps:
Because Android is the most popular mobile operating system, it’s no surprise that it has the most app development support. It provides app developers with access to a plethora of third-party libraries, making it simple to create high-quality apps. The architecture also includes a set of platform APIs that make it simple to implement standard data layer requirements like data storage and retrieval. It gives developers a variety of data storage alternatives, including SQLite, a lightweight database option, and Realm, which provides a smooth API for data storage.
Things to consider before diving into mobile app architectural development:
Better architecture is critical to the success of your project. There are a few things to consider before beginning to develop the app’s architecture.
- Screen resolution
- Screen size
- CPU Features
- Storage Space
- Memory
- Development Framework Availability
Types of mobile app development architecture:
-
Microservice Architecture:
The microservices design separates the application into smaller components known as microservices. Each microservice is totally self-contained and can work independently of any other component. The architecture is the most adaptable and fluid method to software development. This is due to the fact that each app’s functionality may be developed, tested, and deployed independently.
-
Monolithic Architecture:
All app components in a monolithic design are closely integrated and work as a single unit termed a monolith. It’s a strategy that’s common in older systems. The most important justification for using monolithic design is simplicity. Because a monolith has fewer moving components, developers can construct, test, and deploy it as a standalone app more easily.
-
Layered architecture:
Components with similar logic or purpose are grouped and organized into numerous layers or tiers in layered or N-tier architecture. This is the most common architecture for on-premises applications. N-tier applications typically incorporate the three previously mentioned layers: data, business (or application), and presentation. N-layered architecture is simple to understand and administer. With larger programs, it becomes more difficult to determine which layer is causing an error.
Mobile App Development Trends:
Mobile app development trends in 2023 are expanding on a daily basis, with the overall goal of bringing customers together, enhancing contact, increasing security levels, and improving the management system.
Consider the following 2023 trends:
1. 5G: The fifth generation of cellular networks is extremely fast. This will considerably improve speed and dependability. The new 5G speed enables AR/VR, self-driving cars, IoT, and other applications. Future apps will make use of these features to complete things that we had no clue were possible. Furthermore, the fifth generation improves mobile streaming and app functionality by allowing Android app developers to introduce new features without impacting the app’s performance.
2. AI & ML: Today, AI and ML are in high demand. ML (machine language) has reduced the time required to design a mobile app. They can both speed up app development while also reducing errors made by human programmers. Healthcare and retail will see a considerable surge in AI-powered applications during the next 10 years.
3. AR/VR: AR/VR technology has existed since 2020, when COVID-19 began to have an impact on a range of industries, including manufacturing. Several industries began to use augmented reality and virtual reality to construct apps that function as virtual production lines with additional workers. Because of such technology, sales personnel and service providers may now communicate personally with their consumers.
4. Chatbot: It is already widely utilized in the workplace and is required for the creation of Android and iOS applications. Because they deliver faster client replies, Chatbot applications from iOS app development services are often utilized to replace customer care in a variety of ways. It will also become more efficient as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP) advances.
5. Cloud Computing: It is one of the most effective technologies to use in mobile app development. It is no longer necessary to create apps for numerous platforms and handsets. Cloud computing applications can operate in web browsers and work smoothly across different platforms. The cloud-based app’s perfect operation increases mobile speed and ensures that apps on the central server are always available.
6. Cross-Platform Mobile App Development: The development of cross-platform app development is constantly evolving. A development method that allows a company to create and deliver an app across many platforms, including the web. As a result, by developing a single app, you can target both the iOS and Android platforms. The rapid development process is another win-win scenario for creating cross-platform apps.
7. IoT: It is one of the most promising areas in mobile app development, with enormous potential for both users and developers in recent years. It facilitates interaction on multiple levels. IoT technology with internet access is present in almost every gadget. It is useful in a variety of industries, including e-commerce, healthcare, logistics, and others.
8. Progressive Web Apps: PWA is another mobile app innovation that is expected to gain traction in the future. These apps serve as a gateway between native mobile applications and online pages. PWAs take up little space, take less time to load, and are less dependent on the network. Even if they are not a new trend in the world of mobile app development, they are here to stay and help businesses achieve their goals at a reasonable cost
Finally, this blog helps us comprehend the mobile app development architecture in general, as well as its various types and trends in 2023. This will help us even more in implementing the finest development architecture for our mobile app.
Cuneiform Consulting provides advanced solutions to businesses and their employees. Our team of developers is well-versed in mobile app development software and other software development services. So, if you are looking for better app development solutions contact us, and our developers will help you to build the best mobile app.