Successful startups that grow and scale quickly are known as “unicorns” or “billion-dollar companies,” yet this describes just a tiny fraction of all startups.
Scaling and growth are two common buzzwords in the ever-changing business world, yet they refer to quite different strategies for expanding a company. Both growth and success are equally important, but to achieve your business objectives, you need to have a firm grasp of how they vary. Let’s delve into an instructive example to highlight the divergent characteristics of growth and scalability.
Just picture a digital agency that suddenly sees a huge uptick in demand for its successful marketing strategies. Sales, income, and clientele all rise because of this expansion. To keep up with the growing demand, the agency has expanded its workforce, built new facilities, and upgraded its machinery—in other words, it has “scaled” its business.
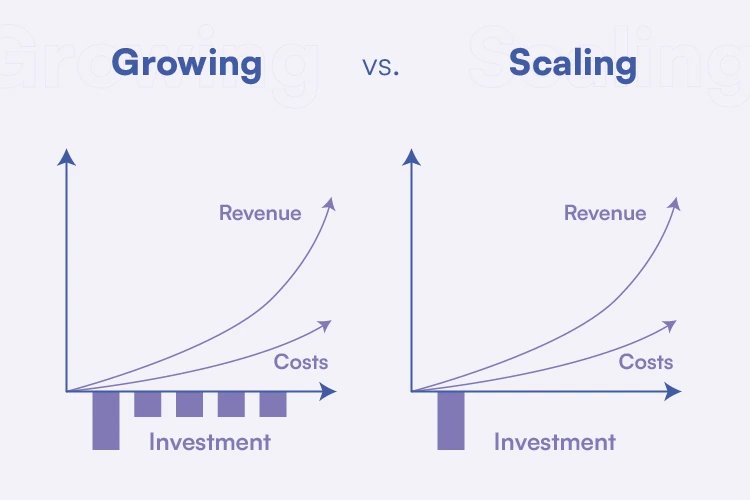
The distinction between growth and scaling is well illustrated here. Growth emphasizes general development and growth, whether measured by income, clientele, or market share. However, scaling places an emphasis on optimizing operations and resources to successfully manage the growing demand without compromising quality or customer happiness.
This blog will go into the minute details of growth and scaling, examining its unique features, advantages, and considerations. Understanding when and how to implement expansion or scaling tactics is essential to achieving your business goals and moving your company forward. If you grasp these ideas, you’ll be in a better position to make strategic and long-term growth decisions.
Come with us as we investigate the intriguing world of growth, tracing the origins of these concepts to their logical conclusions, and examining the strategic avenues that lead to lasting success. Let’s go out on this exciting adventure to learn what differentiates growth from scaling in today’s dynamic business environment.
Definition of Growth and Scale:
Harvard Business Review found that the inability to successfully scale was the key reason why 75% of venture-backed businesses fail to return cash to investors.
 Growth
Growth
Growth can be defined as an increase in either the scale or rate of activity inside an organization. It typically entails attracting more customers, penetrating new markets, and releasing innovative new offerings. Growth can be organic, meaning it comes organically because of the company’s activities, or it can be driven by strategic initiatives like advertising or forming strategic alliances.
A company’s growth, whether in terms of operations, revenue, or size, is essential to its success. Customer acquisition, market penetration, and new product launches are all viable options. Businesses adopt growth strategies to boost earnings and lay the groundwork for future development. However, expansion often results in more expenses and lower profits in the short term. Maintaining long-term profitability needs strategic planning and management that strikes a balance between expanding the business and keeping costs in check.
E.g., a prime illustration of expansion is Uber. When Uber enters a new market, it recruits a larger pool of drivers to serve the area. As a result, the value of profits will grow, but not at an exponential rate.
Scale
On the other hand, scale is defined as the extent to which an organization may raise its output or distribution of a good or service without correspondingly raising its unit expenses. To put it another way, it’s all about doing more with less so that more people can be served. Scaling up often necessitates the use of technology, the adoption of new procedures, or both.
The ability to scale, or increase output or distribution without correspondingly rising expenses, is fundamental to the success of any firm. It entails making investments in technology, automating operations, and increasing productivity. Companies with solid financial footing, efficient procedures, and replicable capabilities can build scalable growth models that can support rapid expansion. Long-term success requires an emphasis on efficiency, investment in technology and infrastructure, and the construction of a foundation of replicable capabilities.
E.g., Google is a great example of a company that has successfully scaled. Google was able to enhance its profits by encouraging companies to advertise their wares on SERPs (search engine results pages). Advertisers only pay when their adverts are clicked.
Both PayPal and Salesforce have accomplished this with comparatively little capital expenditure. By lowering prices and rewarding current customers for bringing in new ones, PayPal was able to expand its user base. This method resulted in a daily rise of 10% in PayPal’s user base.
Benefits of Growth and Scaling
“Scaling doesn’t come from memorizing a list of tactics; it comes from knowing principles.” – Reid Hoffman, Co-founder of LinkedIn
Businesses can profit in numerous ways from expansion and scaling, which in turn contributes to those businesses’ success and continued viability over the long run. Let’s look at the beneficial elements of each option:
Growth:
| 1 | Enhanced Profits and Market Penetration: | Increasing sales and visibility in the market are at the heart of any successful growth strategy, as these factors directly contribute to a company’s bottom line. Businesses can maximize their earnings potential by expanding their consumer base and entering new markets. |
| 2. | Increased Brand Awareness: | Brand awareness usually rises in tandem with a company’s expansion. By entering new markets and growing their consumer base, businesses can increase their brand’s exposure and solidify their position in existing ones. |
| 3. | Economies of Scale:
|
As a company expands, economies of scale allow for greater efficiencies in operations, leading to higher profits. Businesses can reduce per-unit costs, improve terms with suppliers, and maximize the use of available resources by increasing production volumes and expanding operations.
|
| 4. | An Edge Over the Competitors:
|
When a company expands, it earns a strategic advantage by gaining market share faster than its competitors. To maintain their status as market leaders and grow their client base, businesses need access to more capital, a wider range of consumers, and stronger brand recognition. |
Scaling:
| 1. | Effectiveness in Operation
|
Businesses can maximize their efficiency and effectiveness by scaling their operations. Increased demand can be met without jeopardizing product quality or customer happiness if businesses streamline their operations, invest in automation, and make use of available technologies. |
| 2. | Enhanced Customer Experience:
|
The ability to scale helps firms provide better service to their clientele by ensuring high-quality products, prompt shipping, and competent help desk staff. Businesses can better meet client expectations and cultivate loyalty if they optimize their processes and resources. |
| 3. | Profit Maximization:
|
By boosting income and minimizing expenses, scaling helps businesses become more profitable. When organizations have scalable processes in place, they can handle rising sales volumes without experiencing a corresponding increase in costs. |
| 4. | Adaptability and flexibility:
|
The ability to scale helps firms adapt to new opportunities and shifting markets. Companies may more readily adjust to changes in the market, meet the demands of their customers, and roll out innovative new products and services if they have an infrastructure that is flexible and extensible. |
| 5. | Bringing in investments and partnerships:
|
Investors and business partners may be enticed by a well-executed plan for increasing operations. Investors are more likely to put money into a company if they can see that it has room to expand and flourish in the future. Growth also presents opportunities for strategic alliances, joint ventures, and distribution deals. |
Key Differences Between Growth and Scaling:
| Growth | Scaling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
How to Grow or Scale a Business?
“Growth is never by mere chance; it is the result of forces working together.” – James Cash Penney, Founder of JCPenney
There are distinct differences between growing and scaling a business. Here is a breakdown of the most important aspects of growing and scaling a business:
How to Grow a Business?
-
Market Expansion:
Find ways to reach a larger audience by focusing on a different set of consumers, regions, or marketplaces. Create advertising campaigns that connect with these new demographics and modify your offerings accordingly.
-
Innovation in Products and Services:
Maintain a competitive edge by consistently innovating and upgrading your products and services to fulfill the needs of your customers. To add new features, variants, or complementary products/services, it is important to conduct market research, collect client feedback, and invest in R&D.
-
Customer Acquisition:
Take advantage of successful marketing and advertising techniques to expand your clientele. Use a variety of methods like advertising, networking, social media, and digital marketing to get your name out there and attract potential customers. Create a memorable brand name, effectively convey your value offer, and cultivate relationships with prospective clients.
-
Efficient Operations:
Streamlining processes might help you save money while doing more. Find places of waste or inefficiency and seek to optimize workflows and automate procedures wherever possible. Productivity, customer satisfaction, and financial success can all be boosted by streamlining business operations.
-
Strategic Collaborations
If you want to speed up your progress, you should look for ways to collaborate and form partnerships. Discover partners in your industry or that offer related products or services so that you may work together on marketing, product development, or customer acquisition.
How to Scale a Business:
“Scaling is not a destination; it’s a continuous journey of adaptation and evolution.” – Unknown
-
Scalable Business Architecture:
Examine your company’s model to see if it may be scaled. In order to keep up with rising demand without compromising profits or the quality of your service to existing customers, you should examine your various income streams, price structure, distribution networks, and operational processes.
-
Infrastructure and Resources:
Invest in the infrastructure, systems, and tools that will help your business scale. This may involve hiring and training new, qualified workers, acquiring additional funds or financing, and increasing manufacturing capacity and technology systems. Make sure that your current capacity can be expanded without sacrificing quality or productivity.
-
Systematized Procedures:
Maintain uniformity and ease expansion by standardizing and documenting critical procedures. Develop SOPs that define ideal behaviors, workflows, and quality assurance checks. This allows for fast growth, consistent product/service delivery, and easy onboarding of additional staff.
-
Enabling Technology:
Automate and simplify tasks by using technology. Adopt scalable applications in key business functions like customer relationship management (CRM), inventory management, financial management, and data analytics. Efficiency, scalability, and the ability to make decisions are all boosted by technological advancements.
-
Upselling and Customer Retention:
Maintain your current clientele and increase their lifetime worth. Strategies such as tailored communication, loyalty programs, and excellent customer service can be implemented to help retain customers. Sell complementary goods and services to your current clientele to increase your revenue.
-
Continual Enhancement and New Developments:
Create an environment where people are encouraged to think creatively and improve processes on a regular. Inspire them to pitch in with suggestions, try out novel techniques, and welcome change. To keep ahead of the competition, it’s important to anticipate market shifts and adjust plans accordingly.
Conclusion:
To recap, growth and scaling both necessitate long-term thinking, close monitoring, and flexibility. Scaling is the process of improving an organization’s ability to meet rising demand while growth is the process of growing the firm itself. Sustainable growth and long-term success can be achieved when growth methods are combined with scaling endeavours.