Long ago, Google developed Glass, a high-tech eyewear. Google’s cutting-edge, futuristic, “moonshot” technology. The idea behind the creation was brilliant, but the final product was disappointing. The product was panned across all aspects, from cost to security. The product was promoted as cutting-edge technology from the future.
Google exaggerated the benefits of its goods while concealing the market’s flaws. Google Glass was doomed because of this. But how come Google Glass, with all its enthusiasm and cutting-edge technology, was a complete flop? Why most people were reluctant to buy this new type of holding gadget despite its obvious usefulness?
There could be a number of factors at play that end in failure. Lack of clarity led to Google Glass’s demise. Designers of Google Glass did not provide a clear definition or validation of the product’s intended solutions or uses. Google Glass also failed in large part because its creators weren’t clear about the product’s purpose. Designers failed to adequately consider or validate how consumers would put Google Glass to use, nor did they specify what problems it would solve. Consequently, failure to implement MVC was the primary cause.
MVP is strongly related to the failure of google glass. Google disregarded the foundations that any successful business must adhere to, i.e., MVP development. If the right steps had been taken, Google Glass could have been worn as a wearable device with great success.
If you want your business to succeed and avoid the fate of Google Glass, then you need to understand the value of MVP and the best strategy to implement it.
“Problem-solution fit is crucial for the success of any business or minimum viable product.”
Examples of the Most Successful MVPs:
- Airbnb
- Dropbox
- Uber
- Basecamp
- Groupon
- Amazon
Best Strategies for Building a Minimum Viable Product
Begin with Market Analysis:
For a company to succeed, it must conduct market analysis to ensure that its products and services are in demand. Companies can accomplish this by conducting surveys and monitoring the products and services of competitors. It is found in various studies that lack of market need is the leading cause of a company’s failure. Customers won’t go along if the product doesn’t address their concerns.
Create New Ideas That Add Value:
Why should anyone buy this brand new item? What good does it do? In what way does it benefit anyone? These questions can help you figure out what the app’s worth is.
The product’s core estimates should be easily discernible. Even in their most basic form, MVP products should be useful. Create a minimum viable product (MVP) by first identifying user needs.
Sketch out a User Journey:
The design of the MVP is crucial. That’s why it’s important to make the program simple to use. The company should think about the customer’s journey from downloading the app to making a purchase or collecting delivery. User journey guarantees that nothing is overlooked while future product and user satisfaction are taken into consideration.
The stages of a procedure are determined by the user journey. Defining the steps to take in order to succeed is essential. Pay more attention to fundamental processes like finding, purchasing, and getting orders instead of complex features. These are the objectives of the product for the final consumer.
Prioritize MVP Features:
At this point, you should rank all of the features that the MVP will have support for. Questions like, “What do users want?” might help you choose which features should be included in the MVP. Do they stand to gain anything from purchasing this item?
Then, divide the remaining features from the MVP into three groups: high, medium, and low.
Prioritizing these functionalities is another crucial phase in the product development process. Now is the time to start working on a MVP. An MVP prototype can show a business how their ultimate product will turn out.
Prototype your Product:
A business can create an MVP after identifying the product’s essential capabilities and researching the market. Keep in mind that while a minimum viable product (MVP) may not be perfect, it nevertheless needs to satisfy customers. Therefore, it needs to be user-friendly, interesting, and appropriate.
Learn, Build, Measure (B.M.L.)
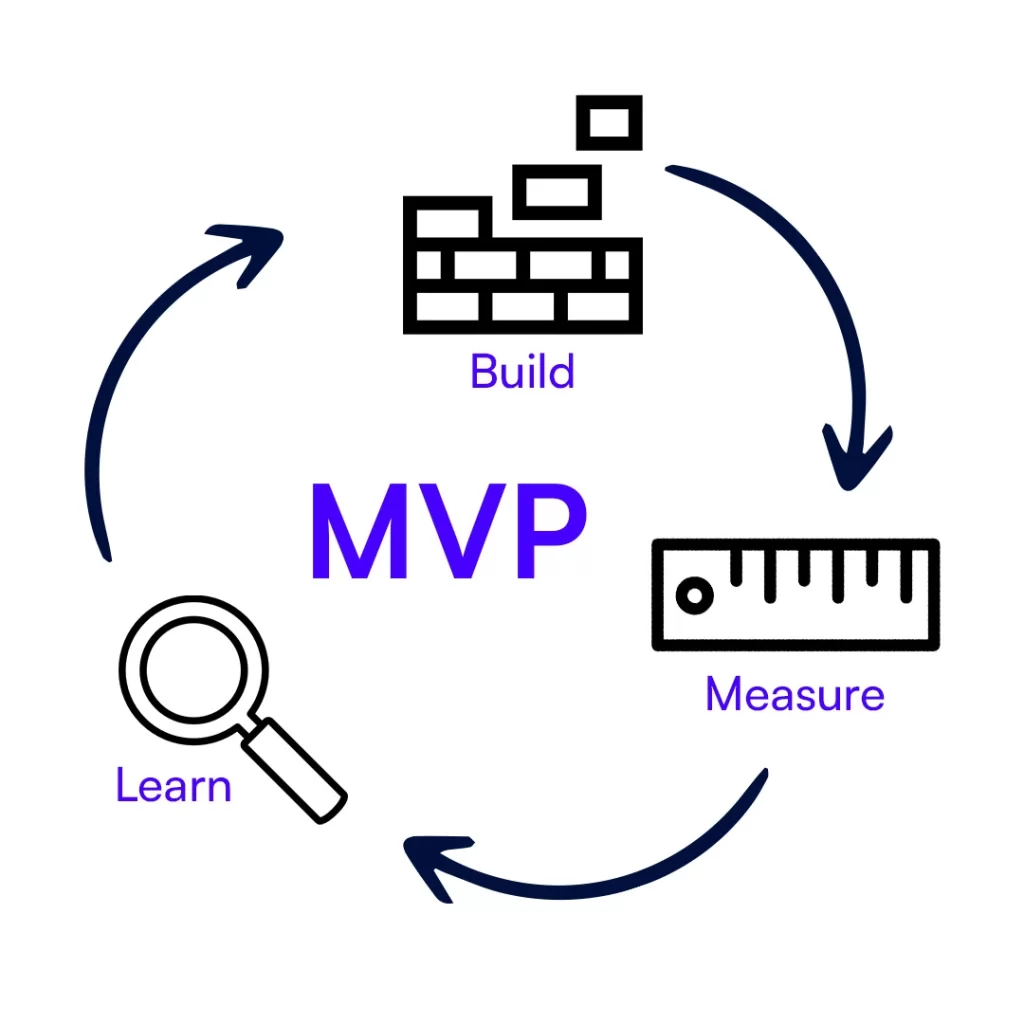
First, decide what the product is going to do, and then create it. Product testing is an essential step following development. Before a product is released to the public, it undergoes rigorous testing by quality assurance engineers.
Afterward, have a look at the minimum viable product.
Conclusion:
It’s from humble beginnings that big things emerge. Construct a minimum viable product (MVP), then test and refine your business model.
A minimum viable product (MVP) is an excellent way to get your product market-fit quickly so that you may gather early client feedback and verify your hypotheses.
Contact us if you have any questions or would like a consultation about MVP development services, including concept development, prototyping, testing, and more.




